Delivery devices work with different flow rates. Below is an image of the fisher and paykel optiflow nasal cannula junior range for.

Leeann Sandberg Nursing Student University Of Penn Nurse Nursing School Survival Nursing Study Guide
The oxygen saturation shall be above the target

Oxygen delivery devices and flow rates nursing. There is a wide variety of devices available to provide oxygen support. Indications for oxygen therapy treatment of documented hypoxia/hypoxemia determined by spo2 or pao2. If a flow greater than this is used, it is uncomfortable for the child and can cause drying and potential bleeding of the nasal mucosa.
The simple face mask is more cumbersome. Oxygen therapy using high flow oxygen delivery devices is considered an advanced nursing competency and is practiced after the nurse has the required education and has had his/her learning validated at the bedside with the appropriate clinical support person. In infants, flow rates shouldn't exceed 2 l/minute.
O2 delivery flow rates chart. Child’s size and tidal volume alter the oxygen concentration child receives despite same flow rate. • this therapy may be beneficial in that nasal interfaces may be better tolerated and children receive the benefits of humidification and likely also receive a low level positive airway pressure.
Nasal prongs are ideal for stable patients who need a low flow of oxygen with a low or medium concentration. An elastic strap stretches over the patient’s head to keep it in place. Reduction and discontinuation of oxygen therapy • oxygen therapy shall be reduced and discontinued in stable patients with satisfactory oxygen saturation.
Oxygen delivery flow rates cheat sheet. A pressure reading (barometer) displays the remaining oxygen pressure in the cylinder, to. This table helps doctors choose the right type of.
Like the simple mask, the nonrebreather mask fits snugly over the patient’s mouth and nose. The flow rate should never be set below 6 l/min because this can result in the patient rebreathing their exhaled carbon dioxide. The aim of this study was to identify the combination of oxygen delivery device, flow rate and device positioning that delivers the highest concentration of wafted oxygen.
May cause drying of nasal mucous membranes, especially at high flow rates. When we apply a nasal cannula, 1 liter per minute is 24% oxygen. High flow nasal prong therapy (hfnp) see the hfnp nursing clinical guideline for more information.
The percentage of oxygen inspired depends on the flow rate and the delivery device; Blenders may be used to wean oxygen titration of flow rates. Oxygen is delivered through different masks, that are attached to an oxygen tank.
Ed nursing staff were surveyed to determine current oxygen wafting practice. • this device is used to deliver high flow rates and high concentrations of oxygen. A simulated patient and oxygen sensor were used to compare wafted oxygen concentrations for six delivery devices in various positions and.
The flow rate can be set on the wall tap: Some patients complain of feeling claustrophobic with masks, and they must be removed before meals. Used to deliver oxygen directly into the nostrils to a maximum flow rate of 2 litres per minute.
This chart is great to have when switching back and forth between cannula and mask for patient comfort. Oxygen delivery devices dr.yusuf imran 2. A regulator is attached to the cylinder's top and works like a tap, allowing the safe adjustment of oxygen flow rate provided, in l·min −1.
This oxygen delivery device is used to deliver high flow rates and high concentrations of oxygen. Then, it goes up by 4% from there. Maximum oxygen flow should not exceed 4 l/min.
Treatment of an acute/emergency situation • dypnoea, tachypnea, bradypnoea, apnea • pallor, cyanosis • use of accessory muscles (nasal flaring, intercostal/subcostal retraction, tracheal tug) • shock/hemorrhage. • wean fio2 first and then flow. Most commonly used oxygen delivery device.
Tube with a mask or nasal cannula). When the tap is manually opened, the oxygen takes the line of least resistance to the patient via an oxygen delivery device (e.g. • nasal high flow oxygen therapy allows delivery of a prescribed fio2 with reduced air entrainment and dilution.
This oxygen delivery devices and flow rates chart shows the o 2 % delivered measured for each tool.

Sat 2 Care U 20 Online Nursing Channel A Guide For Success In All Nursing Officer Exams Nurse Office Nurse Exam

Pin On Ems

Pulmonary Kamp Lecture 6 Oxygen Delivery Non-rebreather Overview Nursing School Lecture Nursingkampcom Nurse Pulmonary Nclex Review

Low Flow Devices Vs High Flow Devices Supportoxygenationrespiratory Respiratory Therapy Notes Respiratory Therapy Medical Knowledge

Pin On Nursing School
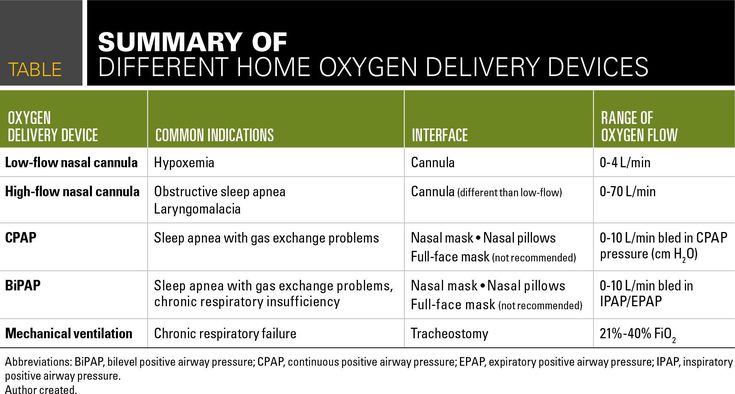
Oxygen Delivery Deviceswhat To Know Respiratory Therapy Student Pediatric Patients Respiratory Care

Pin On Labs

Click Through For The Downloadable Version Of This Click Through For The Downloadable V Nursing School Survival Online Nursing Schools Nursing School Studying

Pin By Lindsay Ieronimo-finn On Respiratory In 2021 Oxygen Nursing School Delivery

Pin On Nursing School

Pin On Rn Stuff

Pin On Nursing Stuff

Respiratory Nursing Respiratory Therapist Student Respiratory Therapy Notes Respiratory Therapy

Pin On Mechanical Ventilation

Pin On Fundamentals Of Nursing

Pin On Rt

Pulmonary Lecture 7 Oxygen Delivery Acute Bvm High Flow Venturi Mask Nur Oxygen Nurse Venturi

Pin By Carey Allen On Respiratory Therapist Icu Nursing Nurse Emergency Nursing

Oxygen Delivery Devices Pediatric Nursing Nursing Tips Icu Nursing